Understanding Skin Conditions & Rashes: Types, Causes, and Treatment
Introduction
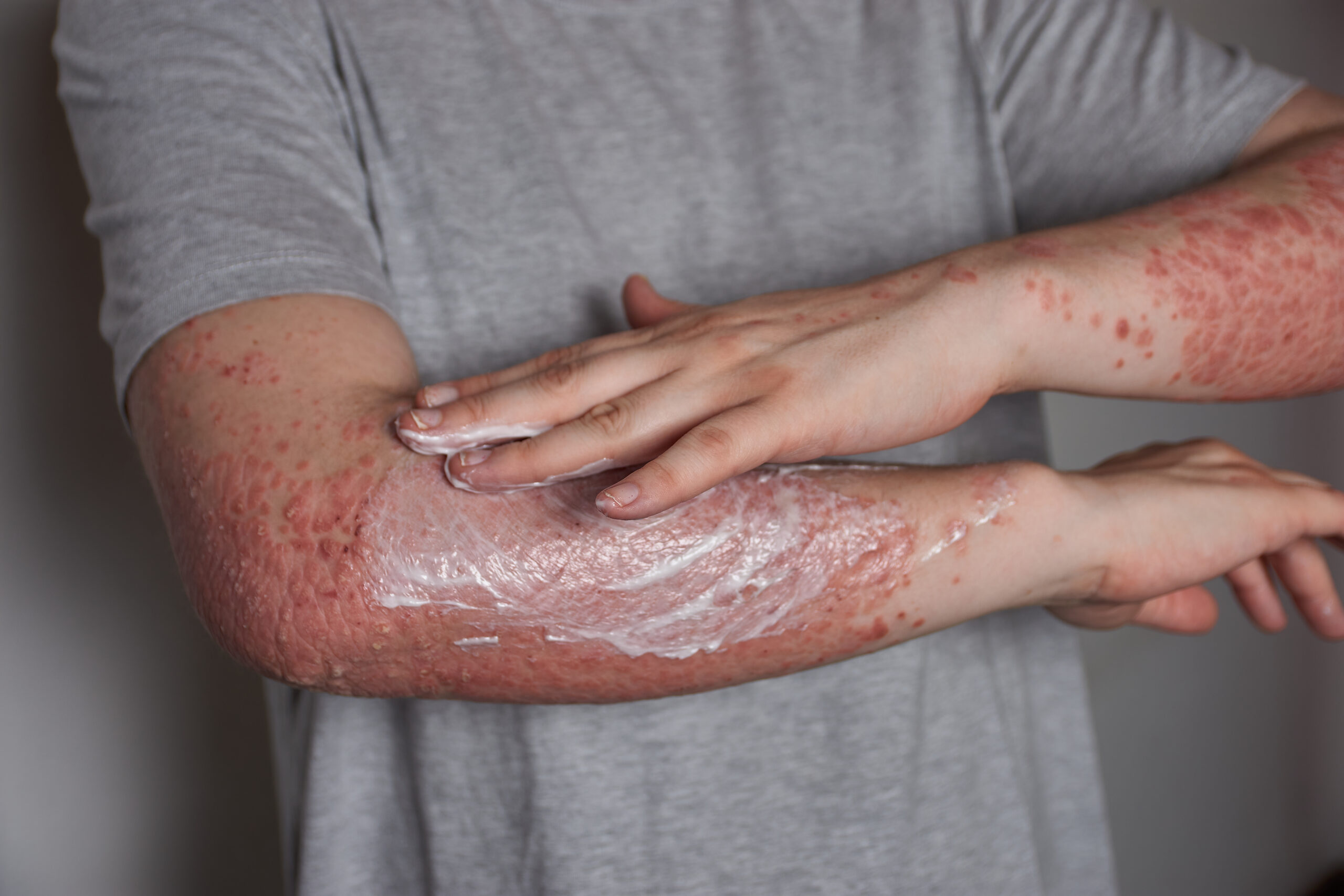
Skin conditions and rashes can appear in various forms, from mild irritations to chronic ailments that require specialized care. Identifying the type and cause of a skin condition is key to effective treatment. In this post, we’ll explore common skin conditions, their causes, symptoms, and possible treatment options.
Table of Contents
- Types of Skin Conditions and Rashes
- Common Causes
- Symptoms to Look Out For
- Treatment and Prevention
- When to See a Dermatologist
- Types of Skin Conditions and Rashes
Different skin conditions present in unique ways, and understanding the symptoms can guide you in seeking proper care. Some common types include:
- Eczema: A chronic condition causing itchy, inflamed skin. It often occurs in response to irritants or allergens.
- Psoriasis: Characterized by scaly, red patches, psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder where skin cells multiply faster than usual.
- Rosacea: A condition that causes redness, usually on the face, and may lead to visible blood vessels and, in severe cases, bumps resembling acne.
- Acne: Often associated with puberty, acne results from clogged pores due to oil, bacteria, and dead skin buildup.
- Contact Dermatitis: A reaction to allergens or irritants, causing redness, itching, and sometimes blisters.
- Common Causes of Skin Rashes and Conditions
Skin conditions can arise due to multiple factors, including:
- Allergens: Ingredients in skincare, clothing materials, or foods.
- Infections: Fungal, bacterial, and viral infections.
- Immune System: Autoimmune conditions like psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor hygiene, diet, and exposure to toxins.
- Genetics: Conditions like eczema often run in families.
- Symptoms to Look Out For
Each skin condition has distinct symptoms, but general signs to watch for include:
- Redness or inflammation
- Itching or burning sensations
- Bumps or blisters
- Dry or scaly patches
- Oozing or crusting
- Treatment and Prevention
Treating skin conditions often depends on the diagnosis. Here’s an overview of options:
- Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments containing corticosteroids or antihistamines for eczema and dermatitis.
- Medications: For conditions like acne and psoriasis, dermatologists may prescribe antibiotics, retinoids, or biologics.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Avoiding known irritants, maintaining good hygiene, and following a skincare routine.
- Home Remedies: Moisturizing regularly, using gentle cleansers, and applying aloe vera for soothing.
- When to See a Dermatologist
Persistent skin conditions, unmanageable symptoms, or sudden severe reactions warrant a dermatologist visit. Early intervention can prevent worsening and long-term damage.
Conclusion
Understanding your skin condition and its causes can lead to effective management and better skin health. If you’re experiencing a skin issue, don’t hesitate to consult a dermatologist for a personalized diagnosis and treatment plan.